Solutions
Solutions to Try Its
1. The first five terms are . 2. The first five terms are . 3. The first six terms are . 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. . 9. The first five terms are .Solutions to Odd-Numbered Exercises
1. A sequence is an ordered list of numbers that can be either finite or infinite in number. When a finite sequence is defined by a formula, its domain is a subset of the non-negative integers. When an infinite sequence is defined by a formula, its domain is all positive or all non-negative integers. 3. Yes, both sets go on indefinitely, so they are both infinite sequences. 5. A factorial is the product of a positive integer and all the positive integers below it. An exclamation point is used to indicate the operation. Answers may vary. An example of the benefit of using factorial notation is when indicating the product It is much easier to write than it is to write out 7. First four terms: 9. First four terms: . 11. First four terms: . 13. First four terms: . 15. First four terms: 17. 19. 21. 23. 25. 27. First five terms: 29. First five terms: 31. 33. 35. 37. 39. 41. 43. First four terms: 45. First four terms: 47.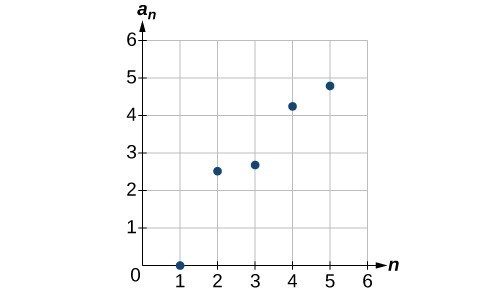 49.
49.
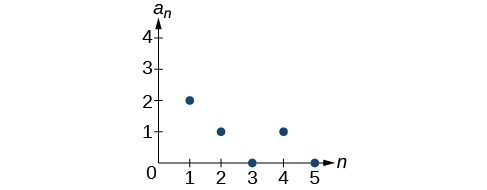 51.
51.
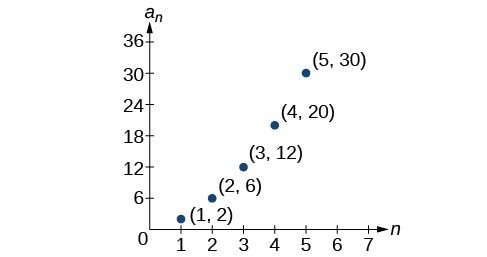 53.
55.
57. First five terms:
59. First five terms:
61.
63. First six terms:
65. First four terms:
67. If is a term in the sequence, then solving the equation for will yield a non-negative integer. However, if , then so is not a term in the sequence.
69.
71.
53.
55.
57. First five terms:
59. First five terms:
61.
63. First six terms:
65. First four terms:
67. If is a term in the sequence, then solving the equation for will yield a non-negative integer. However, if , then so is not a term in the sequence.
69.
71. 